Download these 48 Free Root Cause Analysis Templates in MS Word and MS Excel format to help you conduct your own analysis with ease. You might also be interested to see our collection of Market Analysis Templates and Industry Analysis Templates.
When you are running a business, there are lots of problems and errors, and delays that you handle on a daily basis. Usually, there is always a new mistake or error that stops the entire process or causes a big delay in the execution but occasionally some errors are repeated. Encountering a new problem every time is not the problem because you can only try as much to prevent these problems from happening and the actual issue is seeing the problem repeating itself. This is something that shouldn’t happen and as soon as the problem occurs for the first time, you should take necessary precautions to prevent it from occurring again. Analysis of the basic reason or root cause of the problem is important because it will allow you to see why the problem happened and how it can be prevented in the future.
Contents
Key Elements of a Root Cause Analysis:
- Investigation of the materials and raw materials
- Human error due to lack of knowledge or training
- Problem or defect in the equipment
- Natural disasters that can’t be avoided
- Handling management mishaps
- Information about wrong methods or procedures
- Miscommunication or deliberate negligence
Free Root Cause Analysis Templates
Here is a preview of this Root Cause Analysis Template in MS Word Format,
Application Guidelines for Root Cause Analysis:
- Explanation of the event/problem:
To start a root cause analysis, you first need to explain the incident or event that occurred. This will not only help you understand the event and its various components and elements but also make it convenient for the readers to understand the incident quickly. You can either talk to some eyewitnesses and explain the incident in your own words or ask a witness to write the step-by-step story of the incident for you that you can copy as it is in the analysis report. - Gather the facts and involved causes:
After you fully understand the incident, it’s time to start asking questions and gathering information. The most important part of this step is to gather information about all possible causes and reasons for causing the problem or incident. At this stage, you shouldn’t just focus on a single cause or decide if a particular cause is the key reason for the incident but you need to have an open mind until all the causes and reasons are evaluated. - Find the root cause of the problem:
At this stage when you have the data of all the causes and reasons of the incident, it’s time to look closely and try to find the root cause among all the factors. Although they might look equally important and responsible for causing the incident surely there is a specific cause that triggered the chain reactions of incidents resulting in a big disaster. You need to find that very root cause because if that cause was handled, the whole incident could have been avoided. - Find suitable and applicable solutions:
After finding the real culprit or the root cause for an incident, it’s not that difficult to join heads and come up with possible solutions to prevent the same problem from happening again in the future. Seeing a problem or error is not the issue but letting a problem repeatedly happen is the real big concern. Not only that the solution that you find for the problem should be realistic but it should be applicable as well. - Apply the solution and measure effectiveness:
At the end of the analysis, you should give a conclusion about implementing the solution and its outcome i.e. it has prevented the problem from occurring since then or the solution isn’t very effective so the team might need to come up with a different solution.
Types of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) refers to the process of locating the fundamental reasons for faults/ mistakes/ deficiencies in a particular system, activity or organization. There are different types of RCA which enable the organization or individuals to decide how best to resolve the problem and take appropriate action. There are several steps applicable for conduciton of RCA based on the type of problem, the sector at issue and its level in management.
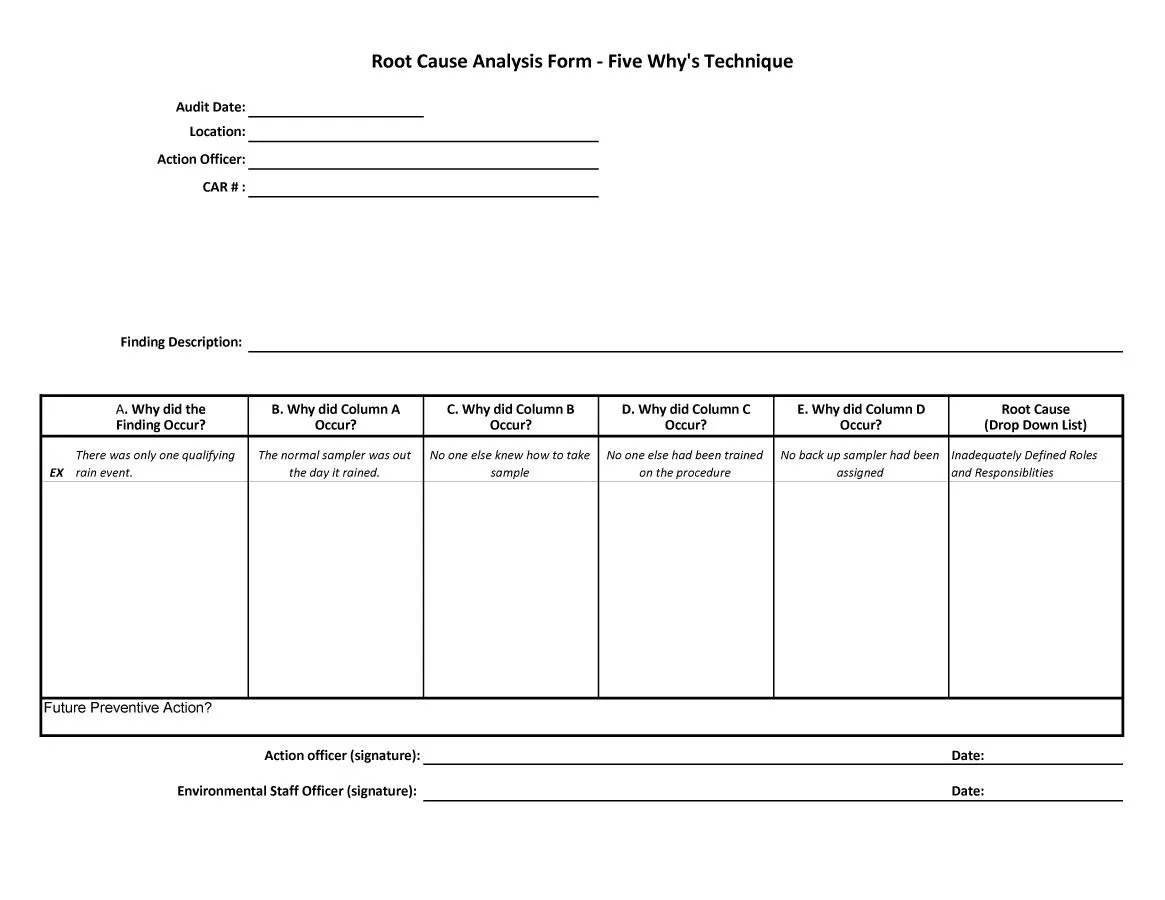
5 Whys Analysis
Root Cause Analysis often is defined and executed by professionals in such a manner that it triggers the repetition of the question “why” until the core reason underlying their discomfited state is understood. With causes of most problems being functional or process-related in nature, this technique comes in handy. It works by getting to the bottom of what an organization believes is its problem and once the boiling point is reached, there is no treatment of the signs as only the causes. And patchwork solutions for laser-targeting only to the causal symptoms are put away. It’s a technique that removes all the complexities of trying to implement a certain process and this problem-solving technique no wonder is a standard practice in drowning out the noise during production, managing projects as well as offering high-quality customer care.
Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
Root Cause Analysis is aided by the use of diagrams such as the Fishbone Diagram or the Ishikawa Diagram. This is how ideas of what could be the reasons for any failings within the system appear on the grounds of dividing them into categories. This method is applicable when there are diverse reasons that are related to different sources. The diagram assumes the shape of diagonally placed bones of fish, where the bones’ head is the problem under investigation and the table consists of branches like people, process, equipment, environment, materials to mention but a few. Given these categories, it can help managers to identify weak links that need enhancement and address the issue rationally.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis is one of the Root Cause Analysis (RCA) facilitators that helps in recognizing a potential problem in the system before it emerges. This technique evaluates how serious, how often, and how likely a failure mode is and assigns a risk score called risk priority number (RPN) on developing the potential failure modes warranting focus. The FMEA method is invented for failure control in safety-critical domains such as aerospace, healthcare, and manufacturing, to mention a few. By forecasting the dangers that may occur, the organizations are able to employ counter-measures against some of the issues waiting to manifest and affect the business.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
As a logical break-down tool, the Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) allows the depiction of the causes of system failures in a tree-diagram structure. It’s effective in identifying the connection between any of the failure points. Engineering, risk management or IT support makes use of FTA which can be useful when various failure factors are considered and their influence on the main problem is analyzed.
Each Root Cause Analysis method has advantages and applies more effectively to some problems than others. Choosing these methods wisely makes sense since problems are correctly identified, which translates into adequate solutions and enhances processes in the long run.